The Reserve Bank of India Framework (2024) on IT Governance, Risks Controls and Assurance Practices is a master directive issued by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). It addresses the escalating threat of cybercrimes and fortify the IT infrastructure within banks and Non-Banking Financial Corporations (NBFCs).
The primary objectives of IT governance include strategic alignment, risk management, resource management, performance management and business continuity/disaster recovery management. The directions will come into effect from April 1, 2024.
Implementation of the RBI framework needs systematic planning and the establishment of a robust IT framework for seamless integration into existing IT infrastructures. Enterprise architects and architecture tools play a key role in constructing the ecosystem within an enterprise. It also aligns with the directive under guidance of enterprise architects and IT managers.
In this blog we will discuss:
- What is RBI Framework?
- Key components of RBI Framework
- RBI Framework and Regulated Entities (REs)
- Importance of RBI Framework
- Aligning Information Technology Risk and Controls strategy with RBI Framework
- Implementing RBI Framework to support your IT structure with ABACUS
- Benefits of using RBI Framework
What is RBI Framework?
The Reserve Bank of India Framework, official known as the “Master Direction on Information Technology Governance, Risk, Controls and Assurance Practices” (DoS.CO.CSITEG/SEC.7/31.01.015/2023-24) is a comprehensive document providing guidelines for regulated entities (REs) in India. It offers extensive guidelines on IT governance and risk management. The framework also covers critical areas like cybersecurity, data management and IT infrastructure.
Key components of RBI Framework
The Reserve Bank of India Framework covers IT governance, IT infrastructure and services management, IT and information security risk management, business continuity and disaster recovery management, and information systems audit.
It also outlines the roles and responsibilities of the board of directors and senior management, IT services management, third-party arrangements, capacity management, and the need for robust IT and information security risk management frameworks.
Additionally, it emphasizes disaster recovery management, periodic review of IT-related risks, and the establishment of a separate information systems audit function.
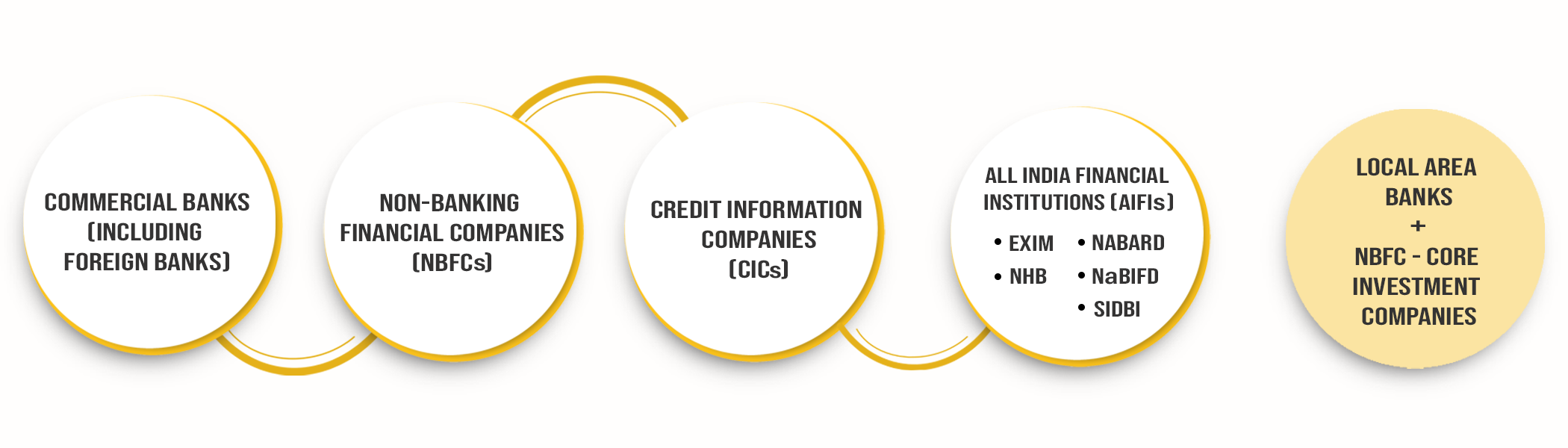
RBI Framework and Regulated Entities (REs)
Entities encompassed by this framework include:
- Commercial Banks (Including Foreign Banks)
- Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs)
- Credit Information Companies (CICs)
- All India Financial Institutions (AIFIs)
- Export Import Bank of India (EXIM)
- National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)
- National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID)
- National Housing Bank (NHB)
- Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI)
There are two entities which are excluded from: Local Area Banks and NBFC-Core Investment Companies
Importance of RBI Framework
The Reserve Bank of India’s framework aim to fortify the IT governance and risk management in the financial sector, steering financial institutions towards enhanced operational resilience and security.
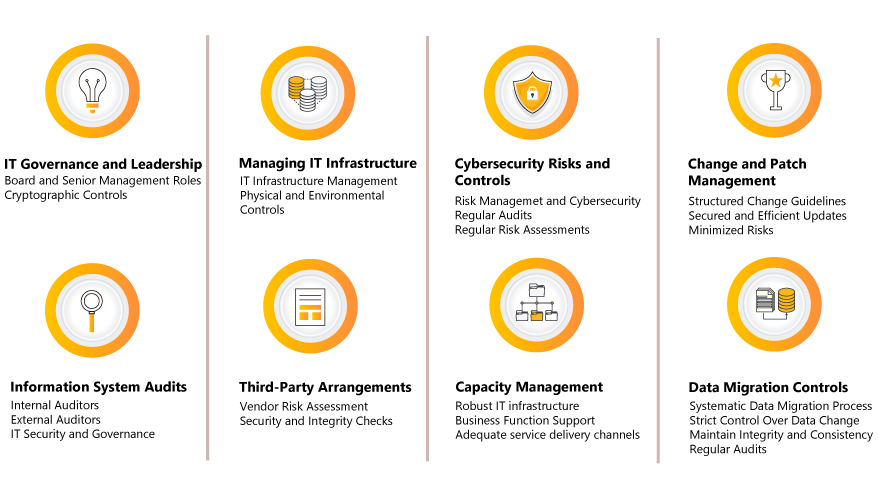
IT Governance and Leadership
The directive emphasizes the critical role of boards and senior management in IT governance. It underscores the importance of establishing committees like ITSC to oversee IT strategies, aligning them with business objectives, and ensuring robust IT governance.
Managing IT Infrastructure
The RBI highlights the necessity of robust IT infrastructure management, emphasizing disaster recovery and business continuity plans. This approach ensures that financial institutions remain operational and resilient in the face of disruptions.
Cybersecurity Risks and Controls
A key focus of the directive is the establishment of comprehensive risk management frameworks. Regular risk assessments and audits are mandated to identify and mitigate potential IT and cybersecurity risks.
The Imperative of Information Systems Audit
The RBI mandates regular information systems audits, involving both internal teams and external auditors. This ensures compliance with the stringent guidelines and enhances overall IT security and governance.
Third-Party Arrangements
The directive also addresses the management of third-party arrangements in IT and cybersecurity, highlighting the need for robust vendor risk assessment processes. This ensures that external partnerships don’t compromise the security and integrity of financial institutions.
Capacity Management
Regulated Entities are required to ensure that their IT infrastructure adequately supports business functions and service delivery channels, adapting to both current and projected needs.
Change and Patch Management
The document stresses the importance of having a structured approach to change and patch management, ensuring that updates and modifications are made securely and efficiently, minimizing risks.
Data Migration Controls
To safeguard the integrity and consistency of data, the RBI mandates a systematic process for data migration, which includes regular audits and maintaining strict control over data changes.
Cryptographic Controls
These controls refer to security measures that involve the use of cryptographic techniques to protect information and communication from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. The directive focuses on the strength of key length, algorithms, cipher suites and applicable protocols used in transmission channels.
Aligning Information Technology Risk and Controls Strategy with RBI Framework
In order to uphold robust IT governance within the framework of RBI, IT Managers can employ various strategies.
One key approach involves the establishment of comprehensive IT governance frameworks and committees. These entities play a pivotal role in formulating, overseeing, and continuously improving the IT strategies aligned with RBI standards.
Organizations also implement specific IT and security policies, practices, and controls designed to mitigate risks and ensure compliance with regulatory guidelines.
In addition, the maintenance of compliance is an ongoing process requiring regular audits, assessments, and reviews. These proactive measures serve to evaluate the efficacy of implemented IT governance frameworks and policies, identify potential vulnerabilities, and ensure adherence to the ever-evolving RBI regulations.
Regular scrutiny not only fortifies the security of financial institutions, it also demonstrates a commitment to maintaining the highest standards of IT governance in the dynamic landscape of the banking sector.
Implementing RBI Framework in Your IT structure with ABACUS
Using a modeling tool like ABACUS for the implementation of Reserve Bank of India framework offers a more comprehensive and interconnected perspective on the current state of IT Governance, Risks and Controls. ABACUS serves as a repository for enterprise architecture, security architecture, and business processes, providing a consolidated view of these critical components.
The up-to-date views available significantly enhance your team’s capacity to identify vulnerabilities, monitor the progress of implementation, and ensure the seamless adoption of the RBI framework.
In ABACUS the directives under each RBI chapter will be translated into actionable capabilities that are implementable on key domains in EA spectrum. Compliance status and scoring algorithms can be user defined to track ownership, monitor progress, present overall fulfilment status of directives on high level yet able to drill down to surface tasks for improvements.
Below is an example dashboard. The scatter graph helps determine the priority levels of topics and the relation between implementation benefit and difficulty. The Graph View is useful in understanding the different topics in a particular chapter and their interdependencies. Overall, the RBI framework dashboard provides a holistic view of what is outlined in the framework and the processes required to accomplish the task.
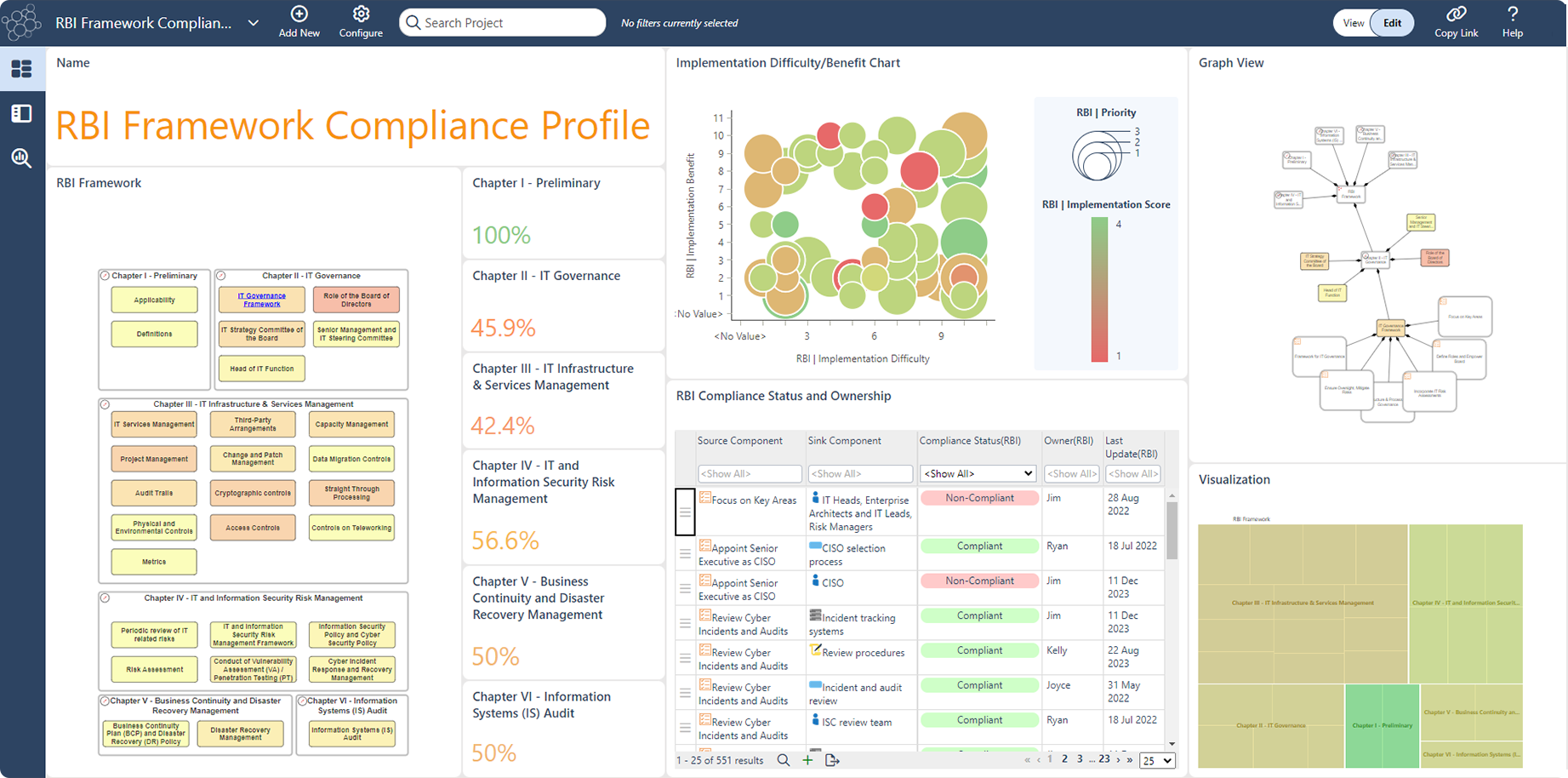
Above: RBI Framework Dashboard in the ABACUS enterprise architecture software
The RBI Framework can be integrated with other frameworks such as ITIL, COBIT, TOGAF, BIAN, NIST. ABACUS supports the seamless integration of these frameworks.
For organizations with existing EA development, the RBI framework can be seamlessly integrated with any existing metamodel; For others new to EA practice, the RBI framework can be deployed in isolation and serves as an “architecture lite” framework for full scope EA implementation because it already covers key domains in EA modeling.
Benefits of using RBI Framework
Safeguarding information technology infrastructure has become an ongoing necessity for all financial services organizations. With cybercrimes reaching unprecedented levels and the continual advancement of technology, architects play a key role in co-ordinating the information needed to protect against threats.
- Ensuring secure and efficient IT systems operations
- Protection against cybersecurity and threat and risk management
- Alignment of IT operations with business objectives and regulatory requirements with the help of enterprise architecture tool
- Facilitation of early EA adoption by implementation modelling in key EA domains
- Consideration of enterprise priorities in the technological advanced era
- Recognition by Reserve Bank of India
The introduction of Reserve Bank of India Framework, continues the central bank of India’s proactive approach to ensuring the resilience and technological robustness of the Indian financial sector while mitigating cyber risks and threats. These guidelines underscore RBI’s commitment to forging a secure yet technologically advanced financial landscape.
The use of enterprise architecture tools, such as ABACUS, becomes instrumental in managing the end-to-end architecture supporting the framework, listing all chapters/guidelines. Dashboards also make RBI framework content accessible with graphs and visualizations which illustrate connections so teams can understand dependencies and risks. By adopting the assured practices outlined in this framework, banks and NBFCs can navigate with confidence towards a more secure and compliant architecture.

